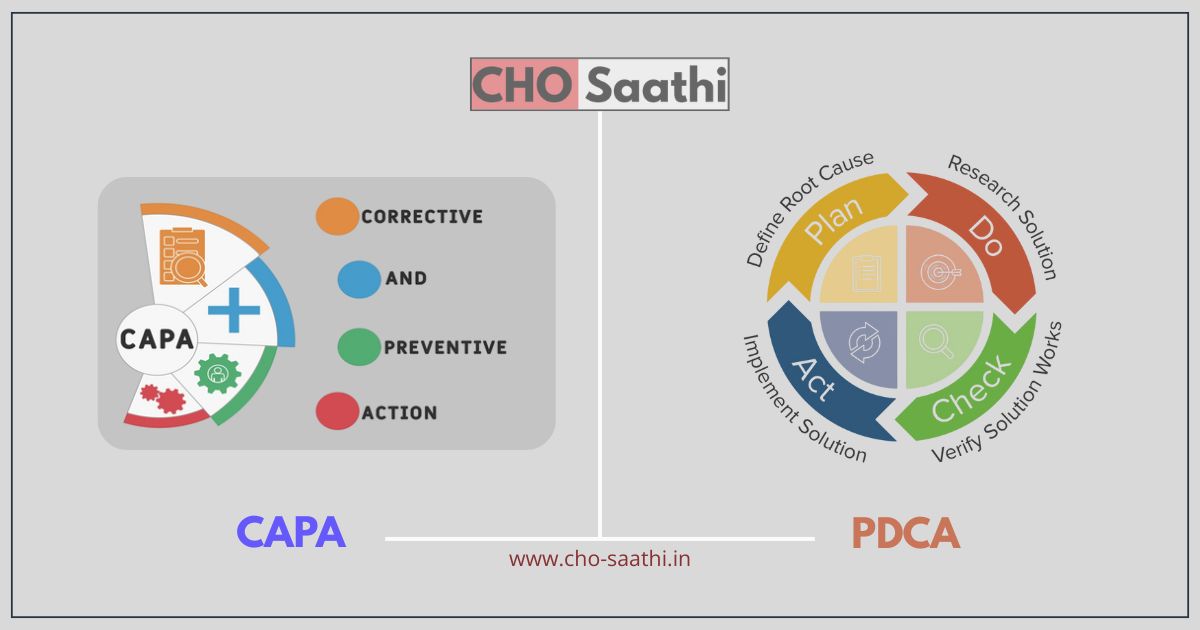
CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions): एक गुणवत्ता सुधार प्रक्रिया है, जिसका उपयोग किसी भी समस्या को ठीक करने और भविष्य में दोबारा होने से रोकने के लिए किया जाता है। जब किसी निरीक्षण या मूल्यांकन के दौरान कोई कमी या समस्या पाई जाती है, तो CAPA दो तरह से मदद करता है: सुधारात्मक कार्यवाही (Corrective Action) से तुरंत समस्या का समाधान किया जाता है, और निवारक कार्यवाही (Preventive Action) से भविष्य में उसी समस्या को रोकने के लिए व्यवस्था बनाई जाती है।
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act): एक निरंतर सुधार का चक्र है, जिसका उपयोग व्यवस्थित तरीके से समस्याओं को हल करने और प्रक्रियाओं को बेहतर बनाने के लिए किया जाता है। PDCA में सबसे पहले योजना बनाई जाती है (Plan), फिर उसे लागू किया जाता है (Do), फिर जांचा जाता है कि परिणाम सही आया या नहीं (Check), और अंत में सफल समाधान को अपनाया या प्रक्रिया में सुधार किया जाता है (Act)। CAPA और PDCA दोनों ही गुणवत्ता मानकों को बनाए रखने और सुधारने के लिए बहुत महत्वपूर्ण टूल्स हैं, खासकर स्वास्थ्य सुविधाओं में NQAS जैसे कार्यक्रमों के तहत।
Learn CAPA & PDCA (In Hindi Language)
1. CAPA (Corrective Action और Preventive Action):
जब NQAS मूल्यांकन के दौरान कोई कमी (Gap) मिलती है (जैसे- एक्सपायरी दवाइयाँ, फायर ड्रिल का रिकॉर्ड नहीं, गंदे शौचालय), तो आपको CAPA फॉर्म भरना होता है। इसमें ये कॉलम होते हैं:
| अवलोकन (Gap) | मूल कारण (Root Cause) | सुधारात्मक कार्यवाही (Corrective Action) | निवारक कार्यवाही (Preventive Action) | जिम्मेदार व्यक्ति | समयसीमा |
|---|
👉 कैसे भरें:
- अवलोकन (Observation):
क्या समस्या मिली?
उदाहरण: “फायर एक्सटिंग्विशर एक्सपायरी हो गए थे।” - मूल कारण (Root Cause):
ये गलती क्यों हुई?
उदाहरण: “फायर एक्सटिंग्विशर की एक्सपायरी डेट मॉनिटर करने का सिस्टम नहीं था।” - सुधारात्मक कार्यवाही (Corrective Action):
तुरंत क्या उपाय किया जाएगा?
उदाहरण: “दो दिनों के भीतर सभी एक्सपायरी फायर एक्सटिंग्विशर बदले जाएंगे।” - निवारक कार्यवाही (Preventive Action):
भविष्य में ये गलती न हो, इसके लिए क्या सिस्टम बनाएंगे?
उदाहरण: “हर महीने फायर एक्सटिंग्विशर की एक्सपायरी डेट जांचने के लिए चेकलिस्ट बनाई जाएगी।” - जिम्मेदार व्यक्ति (Responsible Person):
कौन करेगा?
उदाहरण: “स्टोरकीपर / फैसिलिटी मैनेजर।” - समयसीमा (Timeline):
कब तक पूरा करेंगे?
उदाहरण: “5 मई 2025 तक।”
2. PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act):
PDCA चक्र का उपयोग गुणवत्ता में लगातार सुधार के लिए होता है।
| चरण | क्या करना है | NQAS के लिए उदाहरण |
|---|---|---|
| P (Plan) | समस्या पहचानें और समाधान की योजना बनाएं | “प्रत्येक 3 महीने में आंतरिक ऑडिट की योजना बनाएं ताकि NQAS मानकों का पालन हो।” |
| D (Do) | योजना को लागू करें | “पहला आंतरिक ऑडिट करें और टिप्पणियाँ दर्ज करें।” |
| C (Check) | मूल्यांकन करें कि योजना सफल रही या नहीं | “देखें कि ऑडिट के बाद अनुपालन बेहतर हुआ या नहीं।” |
| A (Act) | सफल कार्य को मानकीकृत करें या सुधार करें | “अगर अच्छा परिणाम आया, तो नियमित ऑडिट पॉलिसी बनाएं, नहीं तो तरीका सुधारें।” |
Also Read: How to Prepare Why-Why Analysis, Brainstorming, and Fishbone for NQAS
📋 CAPA और PDCA के नमूने:
✅ CAPA का उदाहरण (हैंड हाइजीन समस्या के लिए):
| अवलोकन | मूल कारण | सुधारात्मक कार्यवाही | निवारक कार्यवाही | जिम्मेदार व्यक्ति | समयसीमा |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| कर्मचारी मरीजों के बीच में हाथ साफ नहीं कर रहे थे | हैंड हाइजीन पर प्रशिक्षण की कमी | सभी कर्मचारियों के लिए हैंड हाइजीन प्रशिक्षण आयोजित करें | हर महीने हैंड हाइजीन अनुपालन की निगरानी के लिए चेकलिस्ट बनाएं | नर्सिंग अधीक्षक | 1 सप्ताह |
✅ PDCA का उदाहरण (बायोमेडिकल वेस्ट मैनेजमेंट के लिए):
- Plan: कर्मचारियों द्वारा बायोमेडिकल वेस्ट सही से अलग नहीं किया जा रहा। सभी कर्मचारियों के दोबारा प्रशिक्षण की योजना बनाएं।
- Do: सभी विभागों में प्रशिक्षण सत्र आयोजित करें।
- Check: 1 महीने बाद कचरे के डिब्बों का ऑडिट करें।
- Act: अगर गलती फिर भी हो रही है, तो हर डिब्बे के पास रंग-कोडिंग के पोस्टर लगाएं।
🔥 जरूरी टिप:
NQAS अनुपालन के लिए हर कमी (Non-Conformance) के लिए:
- एक स्पष्ट मूल कारण विश्लेषण (Root Cause Analysis) होना चाहिए,
- सुधारात्मक और निवारक कार्यवाही दोनों होनी चाहिए (तत्काल और दीर्घकालिक समाधान),
- साथ में जिम्मेदारी और समयसीमा भी तय होनी चाहिए।
संक्षिप्त और व्यावहारिक भाषा में लिखें — मूल्यांकनकर्ता (Assessor) को यही पसंद आता है।
CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions): is a quality improvement process used to fix problems in a system and prevent them from happening again. When any issue or gap is identified during an inspection or assessment, CAPA helps in two ways: corrective actions are taken immediately to solve the current problem, and preventive actions are planned to ensure the same problem does not occur in the future.
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act): is a continuous improvement cycle used to systematically solve problems and improve processes. In PDCA, first we plan the solution, then we do or implement it, next we check if it worked properly, and finally we act by either standardizing the successful solution or improving it further if needed. Both CAPA and PDCA are important tools to maintain and improve quality standards, especially in healthcare facilities under programs like NQAS.
Also Read:
Learn CAPA & PDCA (in English Language)
1. CAPA for NQAS Assessment:
When a gap is found during NQAS assessment (like expired medicines, no fire drill record, dirty toilets), you have to fill a CAPA form. It has two parts:
| Observation (Gap) | Root Cause | Corrective Action | Preventive Action | Responsible Person | Timeline |
|---|
👉 Here’s how to fill each part:
- Observation (Gap):
What was found wrong?
Example: “Fire extinguishers were expired.” - Root Cause:
Why did it happen?
Example: “No system to monitor fire extinguisher expiry dates.” - Corrective Action (Immediate fix):
What will you do now to fix it?
Example: “Replace expired fire extinguishers within 2 days.” - Preventive Action (Long-term fix):
What system will you create to avoid this again?
Example: “Create a monthly checklist to monitor expiry dates.” - Responsible Person:
Name who will do it.
Example: “Storekeeper / Facility Manager.” - Timeline:
By when it will be completed.
Example: “By 5th May 2025.”
2. PDCA for NQAS Assessment:
PDCA is for continuous improvement. It should look like this:
| Step | What to Do | Example for NQAS |
|---|---|---|
| P (Plan) | Identify the problem and plan the solution. | “Plan a schedule for internal audits every 3 months to maintain NQAS standards.” |
| D (Do) | Implement the plan. | “Conduct the first internal audit and note observations.” |
| C (Check) | Review if the plan worked. | “Check whether compliance improved after the audit.” |
| A (Act) | Standardize success or improve if needed. | “If it worked, make internal audits a regular policy; if not, improve the method.” |
📋 Sample CAPA and PDCA for NQAS:
✅ Sample CAPA for Hand Hygiene Issue:
| Observation | Root Cause | Corrective Action | Preventive Action | Responsible | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staff not practicing hand hygiene between patients | Lack of hand hygiene training | Conduct hand hygiene training for all staff | Monthly monitoring of hand hygiene compliance through checklists | Nursing Superintendent | 1 week |
✅ Sample PDCA for Biomedical Waste Management:
- Plan: Staff not segregating biomedical waste properly. Plan to re-train all staff.
- Do: Conduct training sessions for all departments.
- Check: Audit bins after 1 month.
- Act: If error rate is still high, add color-coded posters on each bin.
🔥 Pro Tip:
For NQAS compliance, every non-conformance (gap) MUST have:
- A clear Root Cause Analysis (Why did it happen?),
- Both Corrective and Preventive Actions (Short-term + Long-term solutions),
- Timelines and Responsibility.
Keep it short and practical — assessors love clear action plans!
Click Here to Join our WhatsApp Channel for more Updates about CHOs.
Click Here to Install the CHO Saathi mobile app for more Updates!
Discover more from CHO Saathi
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







2 Comments